
- HOW TO CREATE EFI SYSTEM PARTITION LINUX INSTALL
- HOW TO CREATE EFI SYSTEM PARTITION LINUX CODE
- HOW TO CREATE EFI SYSTEM PARTITION LINUX WINDOWS
HOW TO CREATE EFI SYSTEM PARTITION LINUX WINDOWS
Make sure your computer is backed up and boot into your Windows environment.Īt the Windows ‘Start Menu’ type ‘cmd’ (or go to Windows They will also appear with their respective distribution identifiers at MX-17 will appear as a listing beginning with ‘MX-17’ or ‘MX17’Īnd select it to boot to the UEFI GRUB menu. If other OSs are installed Post installation, boot to your UEFI firmware setup or boot selection Installs GRUB at the beginning of the root partition–for experts only.
HOW TO CREATE EFI SYSTEM PARTITION LINUX INSTALL
After installingĬritical files, the installer detects your ESP and offers to install Offered selection of MBR partitions in the past. The installer offers selection of your GPT partitions just as it has Secure Boot OFF. Secure Boot ON is the default, but needs to be disabled as it is not supported by MX-17.Native UEFI ON. Make sure that Native UEFI is ON, and any Legacy BIOS compatibility mode is disabled.Your installation media is on USB flashdrive. Fast Boot OFF. UEFI firmware should allow you toĮither disable Fast Boot, or minimize its speed.
Make your changes by access your UEFI firmware Setup The MX-17 64-bit Linux installer requires the following UEFI firmwareĬonfiguration. Sda3…etc., so you can use them for further OS installations as the MX-17 installer will automatically detect theĮSP on sda1, but will also detect additional partitions sda2, Partition–>New to create other partitions for your planned OS andĭata installations.
HOW TO CREATE EFI SYSTEM PARTITION LINUX CODE
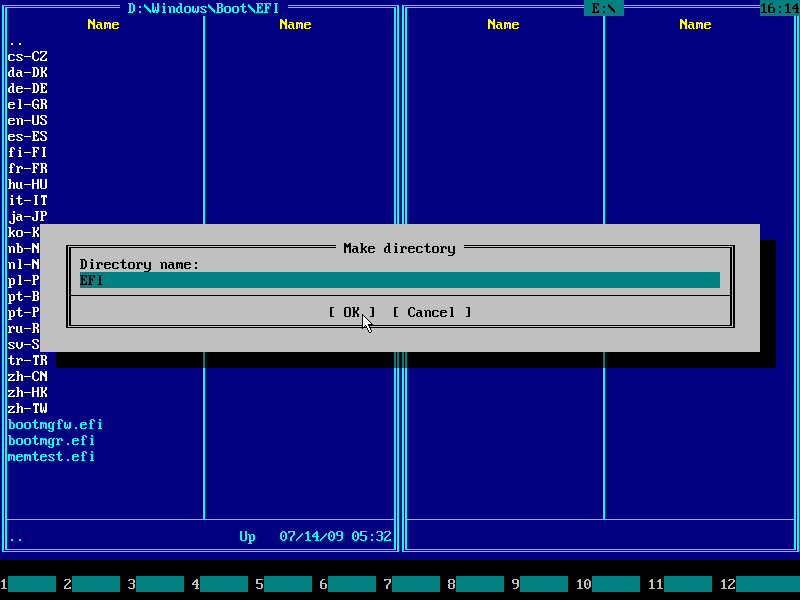
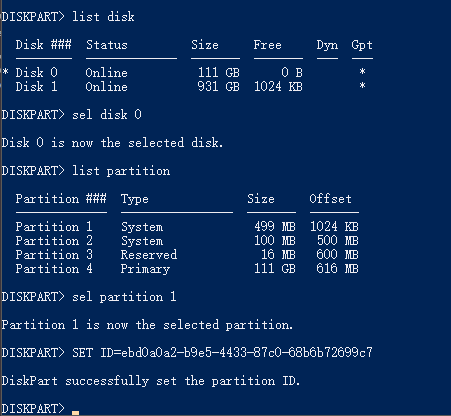
The EFI System Partition (ESP) will be createdĪs sda1 and will store boot code for each OS in use going forward. Then go to Manageįlags and select ‘boot’ and ‘esp’ (‘esp’ should be selected by default Go to Partition –> New to create the first partition, format it asįAT32, and make the size 100 MB (yes, it is small). GUID Partition Table (GPT) partitioning is the modern replacement for Master Boot Record (MBR) partitioning. This step will effectively wipe the disk. Partition Table –>Select GPT instead of MS-DOS from the option pullĭown menu. Operating from DVD or USB, use gparted go to Device –> Create Wipe the disk by creating a new GPT partition table. WARNING: this will effectively remove Windows 10 and make your machine only bootable via Linux Step 1: Removing Pre-Installed Windows 10. No pre-installed OS, should skip to Step 2. Looking to install a LInux-only environment on UEFI-based machines with Machines with pre-installed Windows 10, should start with Step 1. Users wishing to create a Linux-only environment on UEFI-based MX-17 64-bit UEFI Installation Linux-only Environment
Present, MX-17 64-bit supports installations using UEFI boot mode and MX-17 64-bit installation supports two boot modes: Native UEFI & Legacy BIOS.
As a result the following configurations are currently MX-17 is designed to be compatible with UEFI firmware,īut implementations still vary widely among computer and motherboard Specification will offer the ability to emulate or include enough legacyīIOS code to provide compatibility with Linux versions that are ROM), so users should be prepared to study the documentation moreĬlosely here than other firmware options. (Compatibility Support Module), others call it Legacy BIOS OPROM (Option Some implementations call this option CSM Legacy BIOS Compatibility. Options varyĬonsiderably in this area.Since many distributions do not offer the signed code required for This is often the configuration required to boot various Linux OSs, It is important to note that Native UEFI can operate without Secure Boot enabled. To boot Windows 10 products, the ability to disable Secure Boot is oftenĬritical to boot the installation media of some Linux distributions. The ability to disable/enable Secure Boot. To recognize installation or Live media such as USB thumbdrives or This can be important in increasing the ability of the firmware Implementations may offer theĪbility to ‘disable’ or significantly slow the speed of the boot UEFI typically offers the ability to vary Motherboard vendor uses different keys (e.g., Backspace, F2, F12) toĪccess UEFI, but setup is similar to BIOS setup.

Keystrokes during POST (Power on Self Test). Like BIOS, most UEFI implementations are accessible via pre-defined Linux may vary considerably depending on make and model of the computers ButĪt this stage in the deployment of UEFI, many offerings differ in their Microsoft’s Windows 8, most modern PCs now ship with UEFI firmware. In 2005, Intel’s initial specification for EFI (Extensibleįirmware Interface) was contributed to the UEFI Forum which manages and UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) is the replacement for


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
